Introduction to Tokenization and DeFi
Welcome to the Interaxis YouTube channel, where we delve into the fascinating world of blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi). In this introductory section, we set the stage for our exploration into how real-world assets are being transformed through tokenization, and how this revolution is reshaping the landscape of finance.
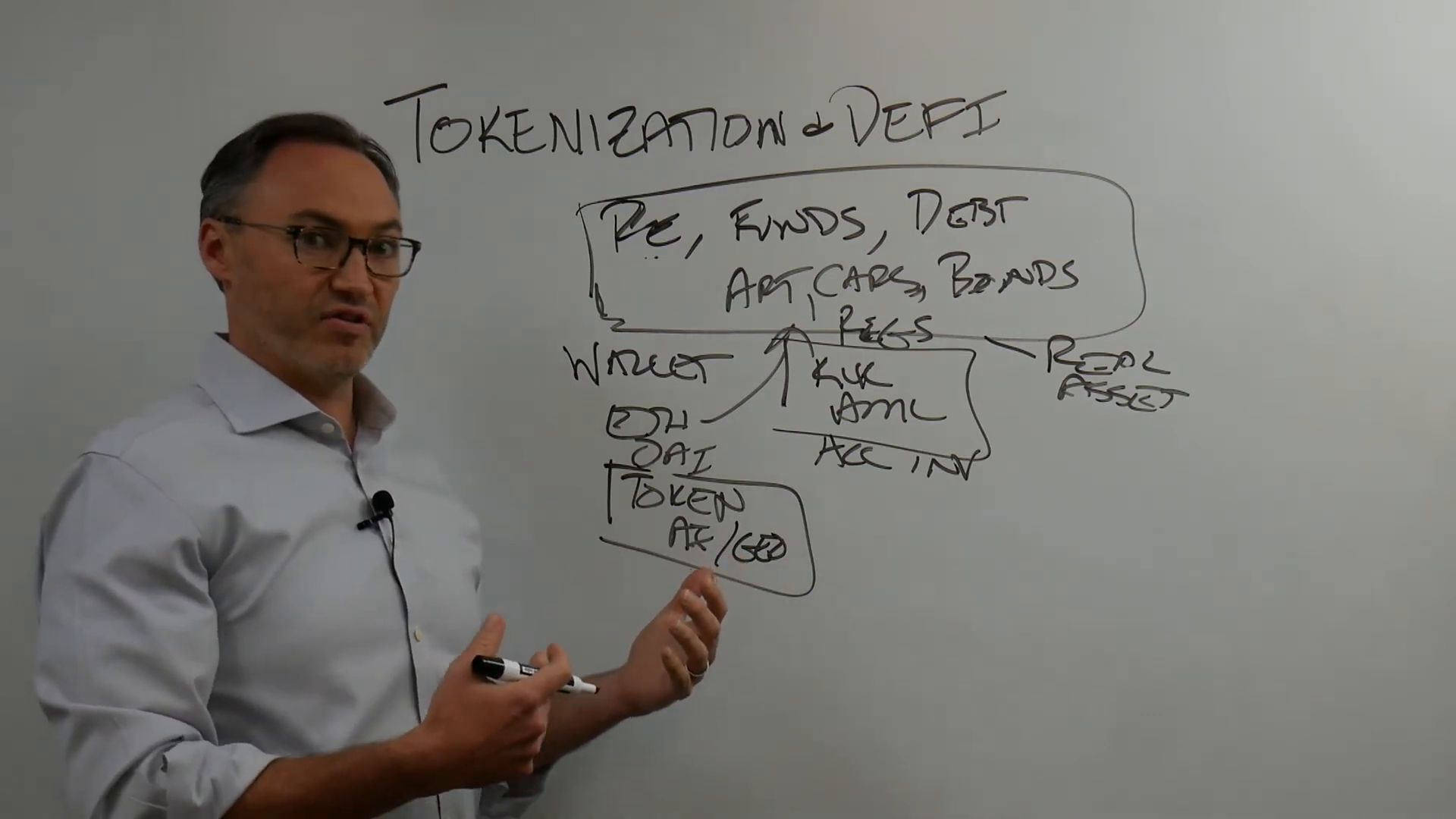
Tokenization refers to the process of converting ownership rights to an asset into a digital token on a blockchain. This innovative approach is unlocking new possibilities for trading and investment by enabling real-world assets, such as real estate, funds, private companies, invoices, bonds, and debt, to be represented on-chain. By doing so, these assets become more liquid and accessible for trading within decentralized financial markets.
The significance of tokenization within DeFi cannot be overstated. It offers novel opportunities for asset diversification and democratizes access to investment opportunities that were traditionally reserved for institutional investors. By putting these assets on-chain, we can enhance transparency and efficiency in financial transactions. In this section, we will explore the foundational concepts of tokenization and its pivotal role in driving the next wave of financial innovation.
The Role of Intermediaries in Traditional Finance
In the realm of traditional finance, intermediaries play a crucial role in facilitating various processes. These intermediaries include banks, brokers, custodians, and other financial institutions that help manage and streamline financial transactions. They are necessary because of the need to outsource trust, data collection, paperwork, logistics, and legal aspects to third parties. Each intermediary charges a fee for their services, which adds to the overall cost of financial transactions.
The need for intermediaries arises from the complexity and the traditional structure of financial markets. They provide a layer of trust and security that is often needed in conventional finance systems. However, this reliance on intermediaries can lead to inefficiencies and increased costs for all parties involved.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) aims to address these challenges by reducing reliance on intermediaries. By tokenizing assets and utilizing blockchain technology, DeFi offers a more streamlined and potentially cost-effective solution. The process of tokenization involves converting physical assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, making them easier to manage and trade.
Tokenization enhances efficiency by making it easier for investors, managers, and issuers to administer investments. The ultimate goal is disintermediation—removing unnecessary middlemen from financial transactions—which can lead to reduced costs and increased transparency.
In summary, while intermediaries have historically been essential in traditional finance for ensuring trust and managing complexities, they also introduce additional costs. DeFi seeks to transform this landscape by leveraging technology to minimize these inefficiencies.

Decentralized Finance and Peer-to-Peer Lending
In the rapidly evolving landscape of financial technology, decentralized finance (DeFi) and peer-to-peer lending have emerged as transformative forces. These innovative concepts challenge the traditional banking system by decentralizing the financial services that have long been dominated by intermediaries such as banks.
Overview of Peer-to-Peer Lending in DeFi
At its core, DeFi aims to replace traditional financial intermediaries with code-driven systems, thereby democratizing access to financial services. One of the standout applications of DeFi is peer-to-peer (P2P) lending, a process that allows individuals to lend and borrow funds directly from one another using blockchain technology. In a typical P2P lending scenario within DeFi, individuals like Adam, who has surplus funds, can lend directly to Ron, who needs to borrow money. This process is facilitated by smart contracts that automate the terms of the loan without requiring a central authority.
Comparison with Traditional Banking Systems
Traditionally, if Adam wanted to lend money to Ron without knowing him personally, both would need an intermediary—usually a bank—to facilitate the transaction. Adam would deposit his money in the bank and earn an interest rate for his deposit. The bank would then underwrite a loan for Ron using Adam’s funds and charge Ron a higher interest rate than what Adam receives. This interest rate differential is how banks earn profits from lending while they also assume the risk of loan defaults.
Moreover, banks play significant roles in verifying borrowers’ creditworthiness and ensuring that lenders’ funds remain secure through mechanisms like FDIC insurance in the U.S., which provides a safety net by guaranteeing certain amounts of deposits.
Benefits of Using DeFi Protocols for Lending
The advent of DeFi protocols revolutionizes this process by removing banks from the equation entirely. By leveraging blockchain technology and smart contracts, P2P lending on DeFi platforms reduces costs associated with loan processing and eliminates banking fees. It also allows for more competitive interest rates by cutting out intermediaries who traditionally take a share of profits.
Furthermore, DeFi protocols enhance transparency and security through immutable blockchain records while offering global accessibility 24/7 without geographical restrictions. This democratization opens up opportunities for individuals in underbanked regions to access credit facilities they might not have had otherwise.
In conclusion, decentralized finance and peer-to-peer lending represent significant shifts from traditional banking operations by leveraging technology to streamline financial processes, reduce costs, and broaden access to financial services.
Tokenization in DeFi: Real-World Applications
Tokenization is reshaping the landscape of decentralized finance (DeFi) by enabling the transformation of tangible and intangible assets into digital tokens. This process allows for the seamless integration of real-world assets into DeFi protocols, bypassing traditional banking systems and introducing a novel way to manage and trade assets.
Examples of Tokenized Assets
In the realm of DeFi, a wide variety of assets can be tokenized. Real estate is a prominent example, where properties can be divided into digital shares, allowing for fractional ownership. This democratizes access to property investments, making it possible for individuals to invest in high-value real estate without the need for significant capital.
Funds are another asset class seeing tokenization. By converting investment funds into tokens, investors gain easier access and greater liquidity. This can also extend to art, automobiles, and even personal debt instruments such as bonds. The potential extends to municipal bonds, corporate bonds, and private debt, which can all be represented as tokens on a blockchain.
Potential Applications in DeFi
Tokenization within DeFi protocols allows users to leverage these tokenized assets as collateral for loans or engage in peer-to-peer lending without the need for traditional banks. Protocols like Compound or BZX have replaced banks by acting as intermediaries that manage these transactions safely and efficiently.
These protocols determine interest rates dynamically based on real-time supply and demand metrics. This level of automation and decentralization not only enhances efficiency but also provides transparency and reduces costs associated with conventional financial systems.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, tokenizing real-world assets comes with challenges. Regulatory compliance is a significant hurdle that must be addressed to ensure legal recognition and protection of tokenized assets. Furthermore, establishing a trustworthy valuation system for these assets is crucial to maintain investor confidence.
In conclusion, while tokenization offers exciting opportunities within DeFi by expanding access to various asset classes and optimizing financial transactions through blockchain technology, it also requires careful consideration of regulatory frameworks and valuation methodologies.

Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
The integration of tokenization into Decentralized Finance (DeFi) brings forward a series of regulatory and compliance challenges that need addressing to fully leverage the potential of this financial innovation. The essence of DeFi is the ability to operate without traditional intermediaries, allowing individuals to manage their assets directly through digital wallets. However, this decentralized nature poses questions around regulatory compliance, particularly concerning Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) protocols.
One of the primary regulatory challenges is ensuring that tokenized assets comply with existing legal frameworks. As DeFi platforms allow for the tokenization of real-world assets such as real estate, debt, and art, they must adhere to regulations that govern these asset classes. This often involves meeting KYC and AML requirements, which can be a contentious point for DeFi users who value privacy and autonomy.
In the future, compliance in a decentralized system might involve innovative approaches such as embedding KYC/AML checks into smart contracts or using tokens that verify an investor’s accreditation status. For instance, an “accredited investor” token could be developed to enable participation in certain investment opportunities without traditional intermediaries.
Additionally, geographic regulations can affect participation in DeFi activities. Different jurisdictions have varying rules about who can invest in certain assets, leading to the potential use of geographic tokens that denote where a user is allowed to invest based on their location or tax residency.
The evolving nature of DeFi suggests a future where compliance mechanisms are integrated seamlessly into the system architecture itself. This could reduce reliance on centralized exchanges or banks, minimizing fees and friction while maintaining necessary regulatory oversight.

The Role of Oracles and Data in Tokenization
In the ever-evolving world of Decentralized Finance (DeFi), oracles and data play a pivotal role in the tokenization process. The flexibility of DeFi allows transactions to occur 24/7, enabling users to purchase tokenized assets like real estate at any time. However, this flexibility comes with certain challenges, such as the lock-up periods specified in offering documents that restrict the sale or use of tokens as collateral within a certain timeframe.
Blockchain platforms like Ethereum and Tezos are instrumental in hosting security tokens. Tezos, for instance, is known for its ability to host security tokens and its growing DeFi capabilities. Cross-chain interactions are becoming more feasible with platforms like Cosmos, which can bridge different blockchains. This interoperability allows users to utilize security tokens from one blockchain as collateral on another blockchain’s DeFi protocols.
One critical aspect that cannot be overlooked is determining the value of these tokenized assets. This is where oracles become crucial. Oracles like Chainlink, Teller, and Band provide real-time data that informs the value of cryptocurrencies and tokenized assets on decentralized exchanges and liquidity pools.
The challenge lies in accurately assessing the value of real-world assets such as real estate. This requires reliable data from trusted providers about various factors like appraisals, occupancy rates, rent payments, credit scores of tenants, and geographical influences. All this data must be aggregated accurately to ensure trust in the token’s value on exchanges.
In conclusion, oracles and trustworthy data are indispensable for ensuring accurate valuation within DeFi ecosystems. As DeFi continues to integrate more real-world assets into its framework, the role of oracles will only become more significant.
Integrating Tokenized Assets into DeFi Portfolios
Integrating tokenized assets into DeFi portfolios is a transformative step in modern finance, bridging the gap between traditional assets and decentralized platforms. Tokenized assets, such as real estate and debt, can now be incorporated into DeFi portfolios, allowing investors to leverage the benefits of decentralized finance while maintaining exposure to real-world assets.
How Tokenized Assets Can Be Included in DeFi Portfolios
The inclusion of tokenized assets in DeFi portfolios involves utilizing oracles and third-party data providers. For instance, platforms like Chainlink or Teller play a crucial role in feeding reliable data into the system, enabling accurate pricing of assets like real estate tokens. These tokens are priced based on various factors, including market appraisals and rental income streams. This ensures that investors can make informed decisions without relying on centralized entities.
Tools and Protocols for Managing Tokenized Assets
Protocols such as the Mellon Protocol and Set Protocol offer tools to build diversified portfolios that include tokenized real estate or debt instruments. These platforms provide transparency and automation, helping investors manage their portfolios effectively. By utilizing these tools, investors can create funds that incorporate various hedging strategies, such as investing in specific regions while hedging against commodity price fluctuations.
Benefits of Transparency and Data in Portfolio Management
Transparency is a key advantage of integrating tokenized assets into DeFi portfolios. When raising funds within decentralized systems like Mellon Protocol, showcasing transparency is crucial for gaining investor trust. This involves displaying the underlying data of investments, such as real estate values or debt ratings. By doing so, investors are assured of the integrity and performance potential of their holdings.

In conclusion, integrating tokenized assets into DeFi portfolios not only enhances diversification but also leverages decentralized technology for greater financial inclusion and innovation.
Future of Tokenization and DeFi

The integration of decentralized finance (DeFi) and the tokenization of real-world assets marks a transformative phase in the financial sector. As DeFi evolves beyond mere cryptocurrency trading, it is increasingly relying on real-world assets as collateral for loans, which can then be securitized and tokenized. This shift is poised to bring an unprecedented level of transparency and trust, as investors gain insight into the collateral backing their investments.
However, the realization of this vision requires a robust regulatory framework and secure custodial solutions. The technology must ensure the safety of smart contracts to prevent financial losses, especially when real assets are at stake. The potential democratization of finance could allow broader participation in financial markets, providing access to a wider range of asset classes previously restricted to wealthy individuals and institutions.
As these regulatory and technological hurdles are addressed, the DeFi landscape is expected to expand, offering new opportunities for investors globally. This exciting development underscores the importance of ongoing discussions about tokenization and its potential to reshape finance. We encourage enthusiasts to stay informed about these changes by following relevant channels and joining conversations about this evolving field.










